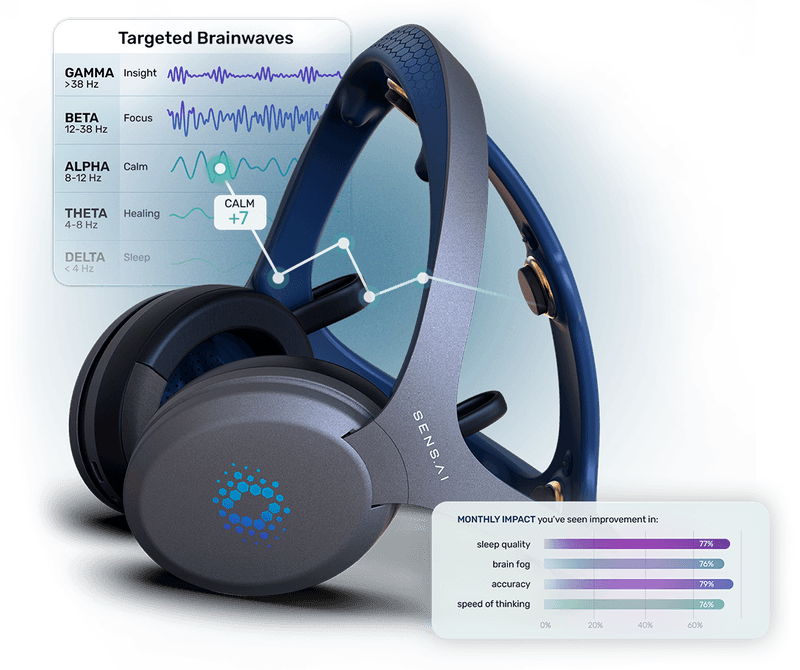
Biological Mechanisms of Action: Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback is a non-invasive, evidence-based technique that trains individuals to regulate their brain activity by providing real-time feedback on their own EEG signals. Through operant conditioning, neurofeedback promotes neuroplastic changes — modifications in brain function and structure that persist over time. These changes are associated with improvements in cognitive performance, emotional regulation, and symptoms of neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Operant Conditioning and Neuroplasticity
Neurofeedback operates through operant conditioning: users are positively reinforced (via visual/auditory cues) when their brain activity moves toward desired patterns. Over repeated training sessions, this reinforcement shapes brainwave activity to reflect more optimal functioning.
- Operant conditioning leads to long-term potentiation (LTP), a core mechanism of synaptic plasticity that strengthens the connection between co-activated neurons.
- Neurofeedback also supports Hebbian plasticity (“neurons that fire together wire together”) by reinforcing repeated activation of desired neural pathways.
Homeostatic Regulation and Compensatory Mechanisms
In cases of abnormal brainwave patterns—such as excessive slow-wave (delta) activity or diminished alpha in aging and cognitive decline—neurofeedback promotes homeostatic plasticity. This mechanism restores balance by downregulating overactive regions and strengthening underactive ones.
For example, increasing upper-alpha frequencies has been shown to correlate with improved memory and attention, particularly in aging and MCI populations.
This compensatory neural rebalancing enhances functional network communication.
Engagement of the Dopaminergic Reward System
Neurofeedback success is often accompanied by a subjective sense of reward or clarity, which reflects activation of the dopaminergic reward system. This activation further strengthens learning and compliance, forming a closed feedback loop that sustains behavioral and neural changes.
This intrinsic reward response helps consolidate training gains and makes neurofeedback both effective and engaging.
Adaptive and Personalized Protocols
Modern systems like Sens.ai enhance classical neurofeedback by integrating:
- Real-time signal processing, including artifact rejection
- Dynamic thresholding based on user progress
- Adaptive algorithms that tailor frequency targets and training duration to the individual
This increases training efficiency, minimizes frustration, and ensures consistent, measurable outcomes.
Applications in Cognitive Longevity and Peak Performance
By targeting specific EEG patterns associated with focused attention, memory consolidation, or meditative states, neurofeedback can:
- Reduce symptoms of ADHD, anxiety, insomnia, and mild cognitive impairment
- Improve executive function, emotional regulation, and self-awareness
- Enhance creativity, flow states, and cognitive endurance
Conclusion
Neurofeedback modifies brain activity through biologically validated mechanisms including operant conditioning, synaptic plasticity, homeostatic rebalancing, and engagement of the brain's reward systems. These mechanisms are well-documented in peer-reviewed neuroscience literature and support neurofeedback's use in both clinical remediation and cognitive enhancement.
Sens.ai builds on this scientific foundation by combining personalized protocols, real-time brain mapping, and accessible home training into a turnkey platform for biological brain age optimization and cognitive resilience.
Ready to try Neurofeedback?
Whether you want better sleep, sharper focus, or to evolve into your highest potential—Sens.ai was built for your journey.