Brain Training
From Mental Noise to Mastery

Brain training isn’t a quick fix—it’s a structured practice that builds lasting skills. Just like physical fitness, the long-term benefits come through repetition and feedback. With the right tools, you can cultivate clarity, calm, and adaptability—and experience the mental gains of a lifetime of meditation.

What Is Brain Training?
Brain training refers to practices that strengthen the brain's ability to focus, regulate emotions, adapt to challenges, and recover from stress. It is not passive tracking, and it’s more than playing games that challenge memory. True brain training relies on neuroplasticity — the brain’s ability to change itself —and delivers lasting improvements through active feedback, skill-building, and repetition.
You can think of brain training as mental conditioning. Just as athletes repeat targeted exercises to improve physical performance, brain training helps reinforce helpful brainwave patterns and cognitive flexibility.
Why Does Brain Training Matter?
Your brain is always changing—either by default or by design. Without intervention, distraction, stress, or poor sleep can hardwire unhelpful patterns. Brain training puts the power back in your hands, helping you actively shape how you think and feel.
This matters whether you’re trying to improve focus, bounce back from burnout, support long-term brain health, or perform at your best. Unlike temporary boosts, training changes traits—not just states.
Four Core Types of Brain Training
Most effective brain training fits into four categories:
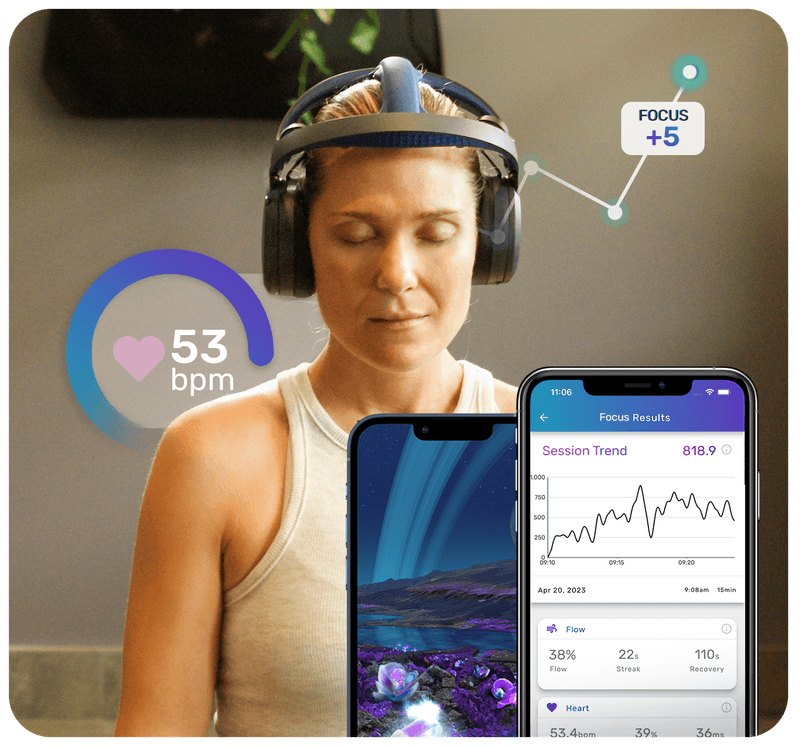
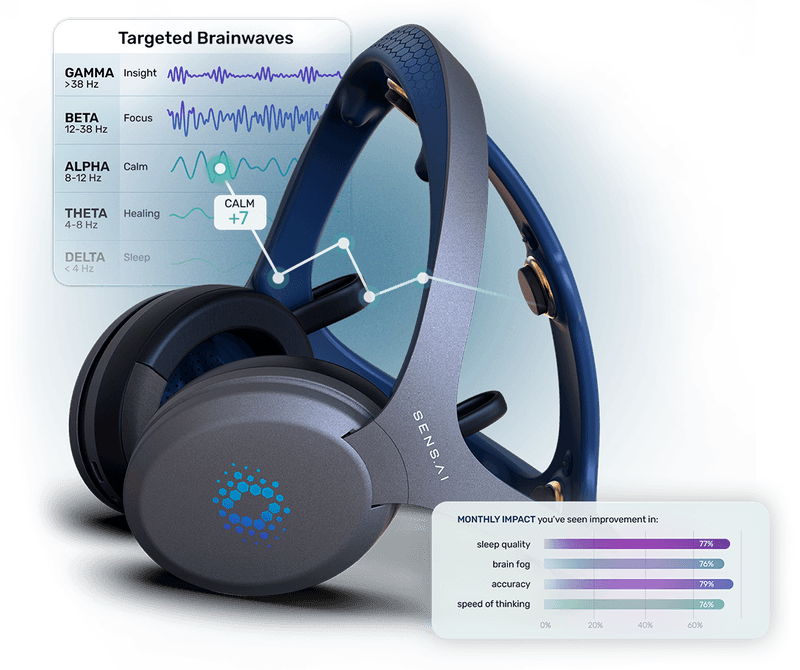
- Neurofeedback: Uses EEG to help you learn how to generate more optimal brainwave patterns. This approach targets attention, calm, or creativity depending on the protocol.
- Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Biofeedback: Helps balance sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems with conscious breathing patterns.
- Meditation & Mindfulness: Strengthens attention and emotional regulation by training the mind to become more aware and less reactive.
- Conscious Breathing – A deliberate breath practice that helps regulate physiology, calm the mind, and support awareness and attention.
More intensive forms of stimulation — such as electrical stimulation or pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) — are typically classified as medical interventions. These can deliver stronger inputs and may require professional oversight.
These forms of training are often more effective when paired and repeated over time.
What Makes Brain Training Effective?
Effective brain training goes beyond entertainment. It:
- Uses real-time feedback so your brain learns what to change.
- Challenges different brainwave frequencies, promoting flexibility across mental states.
- Reinforces lasting patterns — the brain learns by doing, again and again.
- Builds skills that show up in real life, not just in an app score.
This is the key difference between stimulation and training: stimulation helps you access a state; training helps you learn to get there on your own.
How Brain Training Feels
Some sessions feel calm, others energizing. Progress isn’t always obvious in the moment—but like physical fitness, the benefits add up.
Most people notice change outside of the session: staying focused longer, handling stress more smoothly, or bouncing back faster from setbacks. These aren’t hacks—they’re habits your brain is learning to sustain.
Ready to try Brain Training?
Whether you want better sleep, sharper focus, or to evolve into your highest potential—Sens.ai was built for your journey.